Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) has emerged as a crucial treatment option for women experiencing the physical and emotional challenges of menopause. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of MHT, exploring its types, benefits, risks, and considerations for its use.
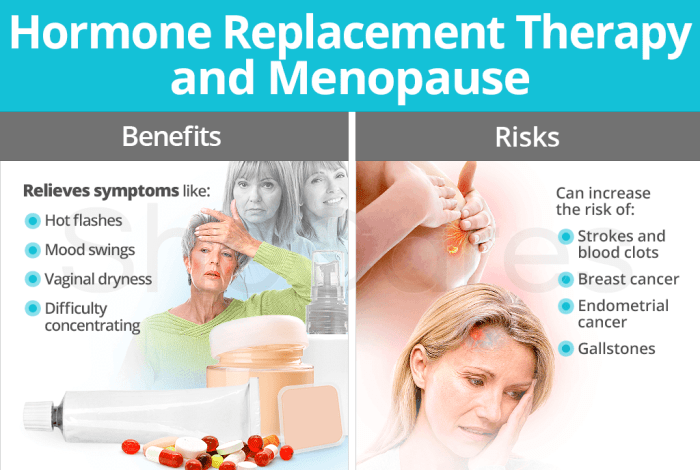
As women navigate the transition into menopause, MHT offers a range of potential benefits, including relief from hot flashes, night sweats, and other bothersome symptoms. However, it’s essential to weigh these benefits against potential risks, such as an increased chance of blood clots or breast cancer.
This guide provides a balanced and informative overview of MHT, empowering women to make informed decisions about their health.
Menopausal Hormone Therapy (MHT)

Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT), also known as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), is a treatment used to relieve symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. It works by replacing the hormones that are lost during menopause.MHT is available in different forms, including tablets, patches, gels, and creams.
The type of MHT that is best for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences.
Benefits of MHT
MHT can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Relief from hot flashes and night sweats
- Improved sleep
- Reduced vaginal dryness
- Prevention of osteoporosis
- Reduced risk of heart disease
Risks of MHT
MHT can also have some risks, including:
- Increased risk of breast cancer
- Increased risk of blood clots
- Increased risk of stroke
- Increased risk of endometrial cancer
The risks of MHT are generally small, but it is important to talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks before starting treatment.
Indications for MHT
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is used to treat a variety of symptoms and conditions associated with menopause. These include hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood swings. MHT can also help to prevent osteoporosis and other health conditions.
Managing Menopause Symptoms
MHT can be an effective treatment for the symptoms of menopause. Hot flashes and night sweats are the most common symptoms of menopause, and MHT can help to reduce the frequency and severity of these symptoms. MHT can also help to improve sleep quality, mood, and energy levels.
Preventing Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle. It is a major risk factor for fractures, which can be serious and debilitating. MHT can help to prevent osteoporosis by increasing bone density. MHT is most effective in preventing osteoporosis when it is started early in menopause.
Other Health Conditions
MHT may also be helpful in preventing other health conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, and Alzheimer’s disease. However, more research is needed to confirm the benefits of MHT for these conditions.
Contraindications and Precautions
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is generally safe and effective, but it’s not suitable for everyone. There are certain conditions that may contraindicate MHT, and it’s important to be aware of these before starting treatment.
Conditions that may contraindicate MHT:
- Active or recent breast cancer
- Active or recent endometrial cancer
- Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
- Severe liver disease
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Active blood clots or a history of blood clots
Precautions that should be taken when using MHT:
Even if you don’t have any contraindications to MHT, there are still some precautions that you should take. These include:
- Starting MHT at the lowest dose possible and gradually increasing the dose as needed
- Using MHT for the shortest amount of time possible
- Having regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your progress and check for any side effects
Importance of regular monitoring during MHT:
Regular monitoring is important during MHT to check for any side effects and to make sure that the treatment is working as it should. Your doctor will typically recommend that you have a mammogram and a pelvic exam every year, and they may also order other tests, such as blood tests, to check your liver function and cholesterol levels.
If you have any concerns about MHT, be sure to talk to your doctor. They can help you decide if MHT is right for you and can help you manage any side effects that you may experience.
Administration and Monitoring
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) can be administered through various routes, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
The most common routes of administration include:
- Oral:Tablets or capsules taken by mouth, providing systemic effects throughout the body.
- Transdermal:Patches or gels applied to the skin, releasing hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Vaginal:Creams, rings, or tablets inserted into the vagina, delivering hormones locally to the vaginal tissues.
- Subcutaneous:Injections given under the skin, providing sustained hormone release over several weeks or months.
The dosage and frequency of MHT vary depending on the route of administration, the type of hormone used, and the individual patient’s needs.
It is crucial to monitor hormone levels and clinical response regularly during MHT to ensure its effectiveness and safety. This may involve blood tests to measure hormone levels, physical examinations, and symptom assessments.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies can provide relief from menopausal symptoms and offer a more natural approach to managing this transition. However, it’s crucial to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Herbal Remedies
- Black cohosh: Reduces hot flashes and night sweats.
- Red clover: Contains isoflavones that may alleviate symptoms.
- Chasteberry: Regulates hormonal balance and reduces mood swings.
Dietary Supplements
- Calcium and vitamin D: Essential for bone health.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Reduce inflammation and improve mood.
- Soy isoflavones: Plant-based compounds that mimic estrogen’s effects.
Mind-Body Therapies
- Yoga and tai chi: Promote relaxation and reduce stress.
- Meditation and mindfulness: Improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety.
- Acupuncture: May relieve hot flashes and mood swings.
Comparison of MHT and Alternative Therapies, Menopausal hormone therapy
While MHT remains an effective option for managing menopausal symptoms, alternative therapies can provide a more natural approach with fewer side effects. However, it’s important to note that these therapies may not be as effective as MHT and require more research to establish their long-term safety and efficacy.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact menopause symptoms:
- Regular exercise: Improves mood, sleep, and bone density.
- Healthy diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall well-being.
- Stress management: Reduces anxiety and improves sleep.
- Adequate sleep: Essential for overall health and mood regulation.
- Smoking cessation: Improves cardiovascular health and reduces hot flashes.
Patient Education and Counseling
Patient education and counseling play a crucial role in the effective management of menopausal symptoms and the safe use of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT). Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive information to patients about MHT, including its benefits, risks, and alternative therapies.
Patient Education Handout on MHT
A patient education handout on MHT should include the following key information:
- Definition and purpose of MHT
- Types of MHT and their uses
- Benefits of MHT, including relief from hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and osteoporosis prevention
- Risks of MHT, such as increased risk of blood clots, stroke, and breast cancer
- Contraindications and precautions for MHT
- Importance of regular follow-up and monitoring
- Alternative therapies for menopausal symptoms
Key Points for Patient Counseling
Healthcare providers should discuss the following key points with patients considering MHT:
- MHT is not a cure for menopause but can effectively manage symptoms.
- The benefits and risks of MHT vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health history, and lifestyle.
- MHT should be started at the lowest effective dose and for the shortest duration necessary.
- Regular follow-up and monitoring are essential to assess the effectiveness and safety of MHT.
- Alternative therapies, such as lifestyle modifications and non-hormonal medications, may be suitable for some patients.
Table Summarizing the Benefits and Risks of MHT
The following table summarizes the potential benefits and risks of MHT:
| Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|
| Relief from hot flashes and night sweats | Increased risk of blood clots |
| Prevention of osteoporosis | Increased risk of stroke |
| Reduced risk of colon cancer | Increased risk of breast cancer |
| Improved sleep and mood | Increased risk of gallbladder disease |
| Vaginal dryness | Increased risk of dementia |
Last Word: Menopausal Hormone Therapy
In conclusion, menopausal hormone therapy is a multifaceted treatment option that can alleviate the symptoms of menopause and improve overall well-being. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the individual risks and benefits of MHT and to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets specific needs and preferences.
By providing a comprehensive understanding of MHT, this guide empowers women to engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers, ultimately enabling them to make the best decisions for their health and well-being during menopause and beyond.
FAQ
What are the different types of MHT available?
MHT comes in various forms, including oral tablets, skin patches, gels, creams, and vaginal rings. Each type has its unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on individual needs and preferences.
What are the benefits of MHT?
MHT can effectively alleviate hot flashes, night sweats, and other menopausal symptoms. It can also help prevent osteoporosis, reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases, and improve mood and cognitive function.
What are the risks of MHT?
MHT carries potential risks, including an increased chance of blood clots, stroke, heart disease, and breast cancer. These risks vary depending on individual factors and the type of MHT used.
Who should not use MHT?
MHT is not suitable for women with a history of certain medical conditions, such as breast cancer, blood clots, or liver disease. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if MHT is right for you.