Mental health and substance use are two sides of a complex and often intertwined coin. This article delves into the intricate connection between these two issues, exploring how they can influence and exacerbate each other, creating a cycle of distress.
Mental health disorders can increase the risk of substance use as individuals seek relief from their emotional turmoil. Conversely, substance use can worsen mental health conditions, leading to a downward spiral that can be difficult to break.
Mental Health and Substance Use
Mental health and substance use are closely intertwined, with each influencing the other in a complex and bidirectional manner. Understanding this connection is crucial for effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of both conditions.
Mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia, can contribute to substance use as a form of self-medication to alleviate symptoms or escape from emotional distress. Conversely, substance use can worsen mental health conditions, leading to increased severity of symptoms, relapse, and impaired cognitive function.
Risk Factors for Mental Health and Substance Use
Numerous risk factors increase the likelihood of developing mental health disorders and substance use problems, including:
- Genetics:Family history of mental illness or substance use disorders increases the risk of developing these conditions.
- Environment:Exposure to trauma, abuse, neglect, or social isolation can increase the risk of both mental health problems and substance use.
- Personal experiences:Negative life events, such as job loss, relationship problems, or financial difficulties, can trigger or exacerbate mental health issues and substance use.
Statistics show that individuals with mental health disorders are more likely to engage in substance use, and vice versa.
Treatment for Mental Health and Substance Use
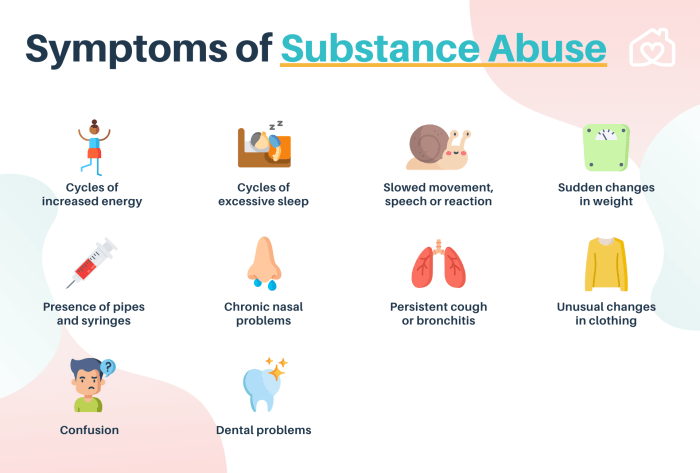
Effective treatment for mental health and substance use disorders requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both conditions simultaneously. Treatment options include:
- Psychotherapy:Talk therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), helps individuals develop coping mechanisms, manage emotions, and address underlying issues contributing to both mental health and substance use.
- Medication:Antidepressants, antipsychotics, and other medications can alleviate symptoms of mental health disorders and reduce cravings for substances.
- Behavioral interventions:Contingency management, motivational interviewing, and other behavioral therapies reinforce positive behaviors and discourage substance use.
Integrated treatment that combines multiple approaches has been shown to be the most effective in improving outcomes for individuals with co-occurring mental health and substance use disorders.
Prevention of Mental Health and Substance Use
Preventing mental health disorders and substance use problems is crucial for public health. Effective strategies include:
- Education:Providing accurate information about mental health and substance use to youth and adults can reduce stigma and promote healthy behaviors.
- Early intervention:Identifying and addressing mental health issues and substance use early on can prevent them from becoming more severe and debilitating.
- Community support:Creating supportive environments in schools, workplaces, and communities can foster resilience and reduce the risk of mental health and substance use problems.
Successful prevention programs have demonstrated significant reductions in mental health disorders and substance use among youth and adults.
Challenges in Addressing Mental Health and Substance Use

Addressing mental health and substance use disorders poses several challenges, including:
- Stigma:Mental illness and substance use disorders are often stigmatized, leading to shame, discrimination, and barriers to seeking help.
- Lack of access to treatment:Many individuals with mental health and substance use disorders do not have access to affordable, quality treatment due to financial constraints, geographic barriers, or lack of insurance coverage.
- Co-occurring disorders:Individuals with co-occurring mental health and substance use disorders face unique challenges in treatment and recovery due to the complex interplay between the two conditions.
Overcoming these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that involves reducing stigma, expanding access to treatment, and providing specialized care for individuals with co-occurring disorders.
Wrap-Up: Mental Health And Substance Use

Addressing mental health and substance use requires a multifaceted approach that tackles both issues simultaneously. By understanding the risks, seeking appropriate treatment, and implementing effective prevention strategies, we can break the cycle and empower individuals to live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
General Inquiries
What are the common risk factors for mental health and substance use?
Risk factors include genetics, trauma, environmental stressors, and personal experiences.
How does substance use affect mental health?
Substance use can worsen symptoms of mental health disorders, trigger new episodes, and increase the risk of developing mental health problems.
What are the benefits of integrated treatment for mental health and substance use?
Integrated treatment addresses both issues simultaneously, improving outcomes, reducing relapse rates, and promoting overall well-being.